| History Timeline of the Powhatan Wars |
History Timeline of the First Powhatan War (1609 to 1614)
|
| 1580 | The Confederacy was founded by Wahunsonacock who became commonly known as Powhatan
| |
| 1606 | King James I of England granted a charter to the Virginia Company to establish colonies in Virginia
| |
| 1607 | The land of the Powhatan Confederacy reached 16,000 miles and the people of its 30 Indian tribes numbered 15,000
| |
| 1607 | May: The establishment of the Jamestown settlement in Virginia run by a council of colonists - refer to Colonial America. The Powhatans inhabited more than 100 surrounding villages. Within 2 weeks of the English arrival, deaths had occurred
| |
| 1607 | Fall / Winter : More than half the colonists die from disease and of starvation. A few Colonist die from wounds caused by Indians.
| |
| 1607/8 | Powhatan, intrigued by the new tools and weapons, helps the Jamestown colony survive with food which they traded for blue beads
| |
| 1607 | Fall / Winter : More than colonists arrive and build St. George’s Fort
| |
| 1607 | December - Captain John Smith was captured by a native hunting party and taken before Chief Powhatan. The daughter of the Chief, Pocahontas (Indian name Matoaka) saves the life of John Smith
| |
| 1608 | January - Captain John Smith is released
| |
| 1608 | September 10, 1608 - the coronation of Chief Powhatan (see the picture following the History Timeline)
| |
| 1609 | May: Lord de la Warr is appointed as the first governor but does not arrive in Virginia until 1610
| |
| 1609 | Tensions between the Indians and colonists rise when livestock, owned by the colonists, are allowed to wander into the Indian cornfields.
| |
| 1609 | 1609 - 1614. The Native Americans reduce trade attempting to starve the colonists out and attacks are made on the fort and the First Powhatan War erupts. The period covering the next 2 years (1609-1610) would become known as the 'Starving Time'.
| |
| 1610 | Acting governor Sir Thomas Gates establishes martial law to maintain order
| |
| 1610 | Spring: Lord de la Warr, the first governor of Virginia arrives
| |
| 1610 | The July 15, 1610: De la Warr sends Powhatan an ultimatum: peace or all out war | |
| 1610 | August 9, 1610: Powhatan does not respond and an impatient De la Warr orders a force of 40 men, led by George Percy, to conduct an attack against the Paspahegh and Chickahominy. This ends in the massacre of women and children
| |
| 1611 | Lord de la Warr becomes ill and leaves Virginia. Sir Thomas Dale and Thomas Gates assume joint governorship
| |
| 1612 | The colonists had learned to cultivate tobacco, which was exported to Europe. This was extremely important as tobacco became the gold of Virginia - it built the economy of Virginia on a single item, tobacco
| |
| 1613 | Pocahontas is captured by the English during the hostilities | |
| 1614 | April: Pocahontas marries tobacco planter John Rolfe. Peace returns to the warring factions
| |
| 1614 | A Peace Treaty ends the First of the Powhatan Wars | |
| 1610 | The July 15, 1610: De la Warr sends the tribe an ultimatum: peace or all out war | |
| 1610 | August 9, 1610: Powhatan does not respond an an impatient De la Warr orders a force of 40 men, led by George Percy, to conduct an attack against the Paspaheghs and Chickahominys. This ends in the massacre of women and children
| |
History Timeline of the Second Powhatan War (1622 to 1632) |
| 1618 | The death of Chief Powhatan. His younger brother Opechancanough assumed full power
| |
| 1621 | Sir Francis Wyatt (1588–1644) is appointed English governor of Virginia. | |
| 1621 | The highly lucrative tobacco crop leads to further encroachment on the Powhatan territories
| |
| 1622 | Chief Opechancanough launches major attacks on the colonists throughout the area, massacring 347 of a total of about 1,200 colonists. This becomes known as the known as the Indian Massacre of 1622 and leads to the outbreak of the Second Powhatan War
| |
| 1622 | The English, in retaliation, order that 3 expeditions should be made each year against the Powhatan to prevent them from planting their crops. The English commanders were forbidden to make peace upon any terms
| |
| 1623 | Opechancanough sues for peace but, in revenge for the 1622 massacre, the English kill a large number of Indians at the Peace meeting
| |
| 1628 | A 'peace' was declared but it was more like a temporary ceasefire | |
| 1629 | The hostilities resumed in March 1629 | |
| 1632 | September 30, 1632: A final peace was made ending the Second of the Powhatan Wars. The Indians were effectively banished from the Chesapeake following this stage of the conflicts
| |
History Timeline of the Third Powhatan War (1644 to 1646) |
| 1641 | Sir William Berkeley replaced Sir Francis Wyatt as Governor of Virginia in 1641. Sir William Berkeley was governor of the colony of Virginia from 1641–1652
| |
| 1644 | Opechancanough mounts a terrifying attack, designed to move the colonists from the Powhatan land, killing 500 colonists.
| |
| 1644 | Opechancanough does not follow-up the attack which allows the colonists to prepare for the third of the Powhatan Wars
| |
| 1644 | The colonists retaliate and march against many of the tribes in the Powhatan Confederacy | |
| 1645 | An additional 3 forts are built in the region to support the Powhatan Wars | |
| 1645 | August: Governor William Berkeley stormed Opechancanough's stronghold and captures and imprisons him. All other captives are sold into slavery during the Powhatan Wars.
| |
| 1645 | Chief Opechancanough refused to admit defeat or sign a Peace treaty. He was shot in the back by an English guard whilst in captivity. With his death the power of the Powhatan Confederacy came to an end as did the Powhatan Wars in 1646
| |
| 1646 | The new Powhatan chief, Necotowance, signed the 1646 Peace Treaty. The result of the Powhatan Wars was a boundary, or racial frontier, between the Indians and English lands that could only be crossed for official business with a special pass. 1646 Treaty Map 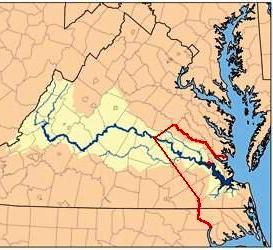
The Red line shows boundary between the Virginia Colony and the
Powhatan Indian tribes, as established by the Treaty of 1646
| |
| 1646 | The situation following the Powhatan Wars lasted until 1677 and the Treaty of Middle Plantation which established the first Indian reservations following Bacon's rebellion.
| |
| History Timeline of the Powhatan Wars |